Fiat Currency Definition
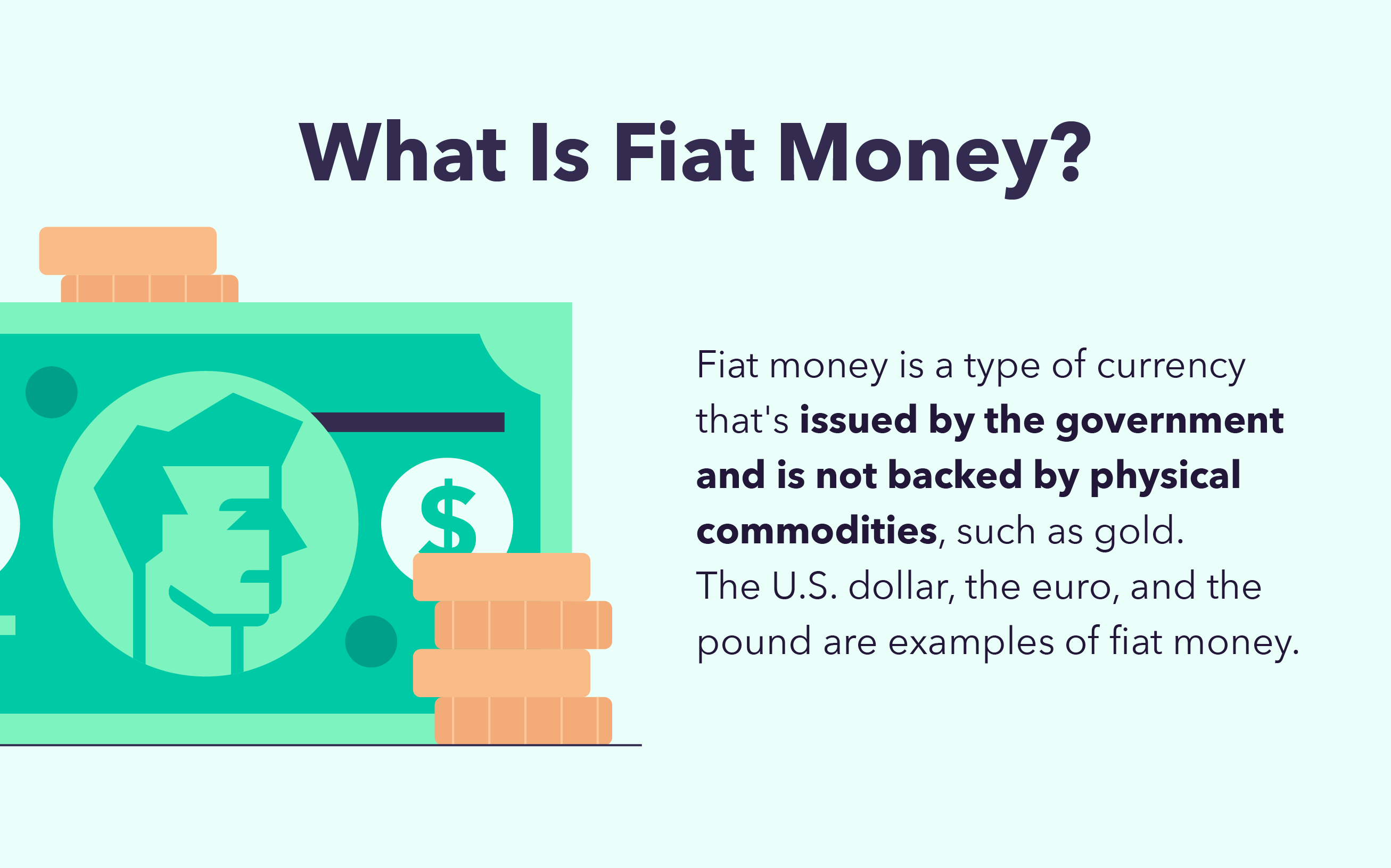
Fiat money is a form of currency issued by a government that is not backed by tangible assets such as gold. Fiat money includes the US dollar, the euro, and the pound.
Could you imagine having to carry gold around with you while you went grocery shopping for the week? Earlier in history, people exchanged gold for products and services, rather than the paper money we are all familiar with today. However, instead of gold, we now exchange items using currencies such as the US dollar, the euro, and even cryptocurrencies.
There are several sorts of currencies available today – some are backed by a government, such as fiat currencies, while others are decentralized and based on blockchain technology, such as cryptocurrencies. This article will discuss the definition of fiat currency, its advantages and disadvantages, and how it varies from other currencies.
What Is Fiat Money?
Fiat currency, or fiat money, is a type of government-issued money that is not backed by tangible assets like gold. Rather than that, fiat money's value is determined by the public's faith in its issuer, the government.
Why is it called fiat currency? The term fiat derives from the Latin phrase “let it be done” or “let it be.” Fiat money has value simply because the government values it, granting the government more control over the currency and the quantity that may be created.
Fiat Money vs. Cryptocurrency
Fiat money is a form of legal tender, meaning it is a currency that has been proclaimed legal by the government and whose value is guaranteed by the issuer (the government). On the other hand, cryptocurrency is a decentralized digital currency that is supported by blockchain technology and is not backed by a central authority such as a government.
In comparison to conventional money, a cryptocurrency is more volatile and provides a better level of information security. Although some predict cryptocurrencies will eventually supplant fiat currencies, the majority of transactions worldwide continue to be conducted using fiat money.
Fiat Money vs. Commodity Money
Commodity money has intrinsic value, which means that it possesses a perceived or genuine worth. This sort of money is made of valuable metal, such as gold or silver. On the other hand, fiat money has no intrinsic value. Consider dollar notes – while they are all printed on the same paper, their worth vary according to what a government believes the cash is capable of being exchanged for.
Fiat Currency vs. Representative Money
The government also creates representative money, but unlike fiat money, it is backed by a tangible product. There are several types of representational money, including credit cards and cheques, that serve as a representation of a desire to pay.
While fiat currency is supported by the government, representational currency can be backed by a variety of assets. A check and a credit card are both guaranteed by funds in a bank account.
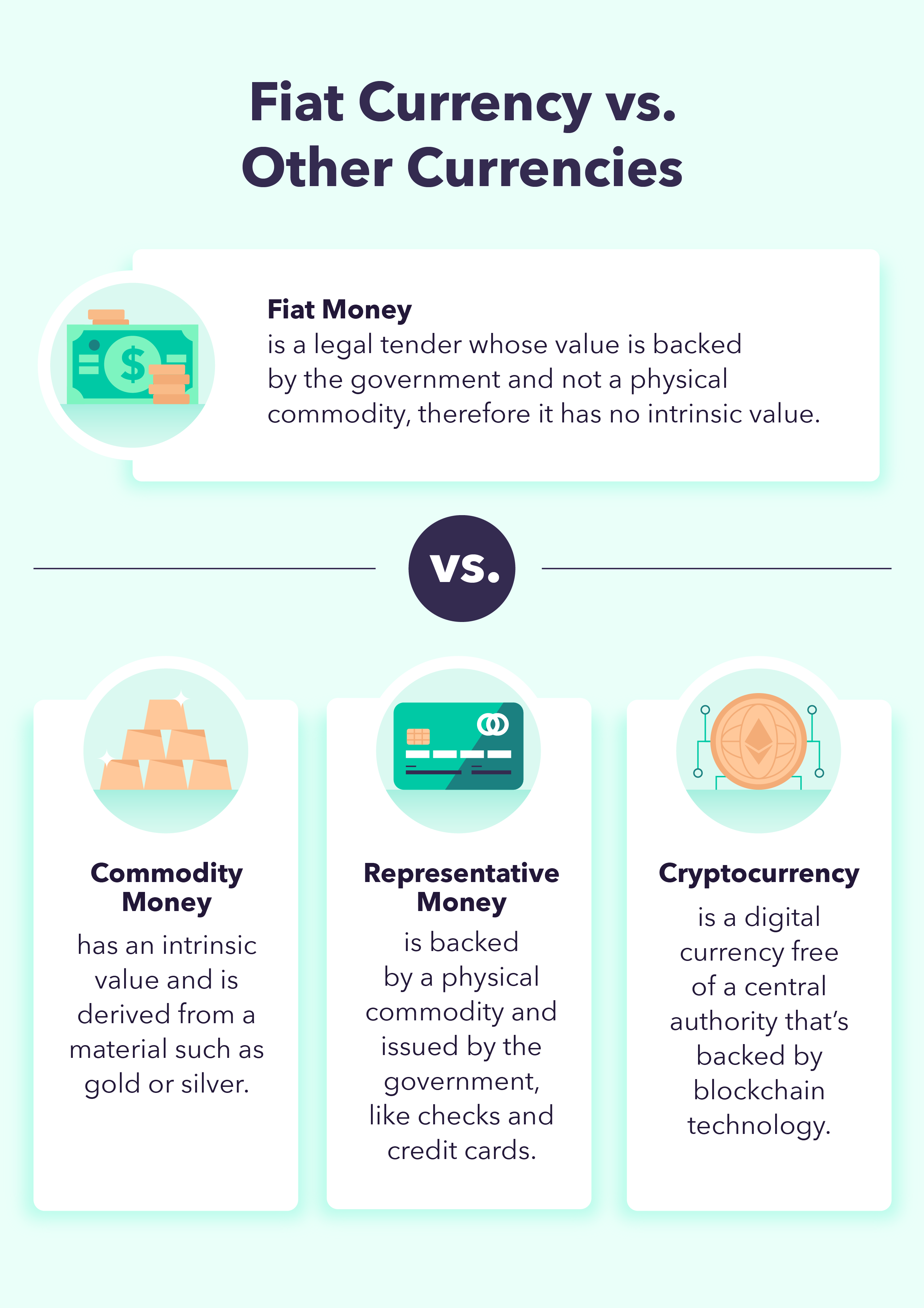
A graphic explains the difference between fiat money and commodity money, representative money, and cryptocurrency.
Understanding Fiat Money in the United States
For the majority of the United States' history, national money was backed by gold and silver. The government enacted the Emergency Banking Act in 1933 in an attempt to re-establish public trust in the national banking system. This legislation would establish a program to restore banking services and eventually phase off the gold standard, which allowed residents to swap cash for gold. From that point forward, the gold standard was entirely supplanted by fiat money: the United States dollar.
Pros and Cons of Fiat Money
Just like other currencies, such as cryptocurrencies, there are some pros and cons to fiat money.
| Advantages of Fiat Money | Disadvantages of Fiat Money |
|---|---|
| Greater control over the economy | Not a foolproof way to protect the economy |
| Cost-efficient to produce | Possibility of hyperinflation |
| Convenient to use | Unlimited supply could create economic bubbles |
Advantages of Fiat Money
Not only is fiat money inexpensive to make, but it is also convenient to carry and trade. However, one of the primary advantages is that fiat money is not backed by a commodity, whereas gold is. As a result, governments have a higher degree of control over the currency supply, giving them the ability to influence economic factors such as interest rates, liquidity, and credit availability.
Because a government controls the money supply, it also has the authority to safeguard the country against financial crises. Indeed, the Federal Reserve Bank of the United States has a dual duty to keep unemployment and inflation low.
Disadvantages of Fiat Money
Although a government has control over its currency supply, it’s still not a guaranteed way to protect the economy from a financial crisis, such as a recession. Another disadvantage of fiat money is that it’s subject to inflation and a government could mismanage and print too much money that could result in hyperinflation.
In addition, the price of fiat money depends on government regulations and fiscal policy, which could result in a bubble with a rapid increase and decline in prices.
The Future of Fiat Currency
Almost every country now has fiat money as a legal tender, so it’s hard to say what’s on hold for the future. Although there is a rapid rise in cryptocurrencies — and some experts believe it could eventually replace fiat currency altogether — fiat money gives governments more flexibility to manage a country’s economy, therefore, we can expect it to stay the primary medium of exchange for years to come.
Sources: GOBakingRates | Federal Reserve History
Frequently Asked Questions About Fiat Currency
The following are some frequently asked questions regarding fiat currency.
What Are Fiat Money's Alternatives?
Nowadays, nearly every country uses fiat money as legal tender. Although gold coins are a possible alternative to fiat money due to their ability to be bought and sold, they are not generally utilized for everyday purchases.
Cryptocurrency is another alternative to fiat money that is gaining popularity. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin may be utilized as the primary form of currency in the future, although they are not generally recognized at the moment.
Why Do Contemporary Economies Prefer Fiat Currency?
Due to the scarcity of gold arriving from mines, central banks were unable to keep up with the increased value. Fiat money was an option that allowed for cost-effective manufacture and ease of use, while also allowing the government greater freedom in managing its own currency.
Is Fiat Currency a Cause of Hyperinflation?
Although overprinting fiat currencies have the potential to cause hyperinflation, the majority of developed countries typically endure modest inflation. Hyperinflation has occurred in the past, even with commodity money, and it is possible that it will occur again if a fiat currency rapidly loses value, like when people lose trust in the nation's currency.
What Is a Fiat Currency?
Fiat currency is derived from the Latin phrase “it shall be,” and refers to a form of currency produced by the government that is not backed by tangible commodities such as gold. Fiat money includes the US dollar, the euro, and the pound.
Bitcoin: Is it a Fiat Currency?
Bitcoin is not fiat money, as it is not a government-issued legal tender. Bitcoin is a decentralized cryptocurrency that is supported by blockchain technology and is decentralized from a central authority.
Fiat Currency Examples
Some examples of fiat currencies are:
- U.S. dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- British pound (GBP)
- Korean won (KRW)
- Japanese yen (JPY)
- Indian rupee (INR)
- Mexican pesos (MXN)
The post What Is Fiat Currency? A Definition + How It Differs From Cryptocurrency appeared first on MintLife Blog.
The post How Is Fiat Currency Defined and Different From Cryptocurrency? appeared first on https://gqcentral.co.uk


Comments are closed